Pod
Pod documentation:
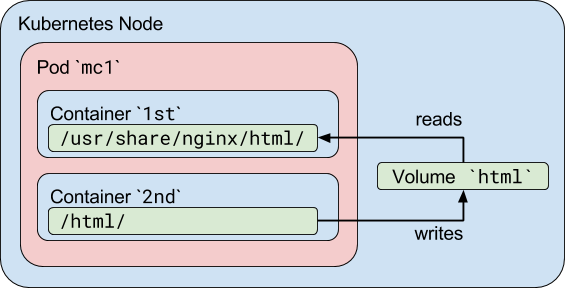
A Pod is a group of docker (or other) containers. Think of a pod as a microservice. A microservice can for instance consist of two containers, one for app logic, and one container for MySQL (for instance).
To show all pods running in your Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl get po --all-namespaces
Containers within a pod share an IP address and port space, and can find each other via localhost.
So in your app, your Java code could connect to MySQL on “jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db”.
Task: Deploy a pod
In a previous exercise, you deployed a Helm Chart consisting of two pods (one front-end and one back-end). A chart is basically just a set of default values for pods (and other resources, like Services). Now we’re going to deploy a pod manually without Helm.
# Watch running pods
watch kubectl get pod
# Open a new terminal and run the pod
kubectl run workshop-frontend --image=torklo/workshop-frontend
NB: watch is not installed on macOS by default. Install it with homebrew: brew install watch (or just use
kubectl get pod -w).
Switch to the terminal where you’re watching the pods, and you should see your pod running! It should like this (the pod’s name will be slightly different):
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
workshop-frontend-868bbdb7f7-7fltf 1/1 Running 0 3m
It’s possible to deploy using a YAML config as well, but that’s out of scope for now.
Task: Access the app
OK, it’s deployed, so let’s access our app, i.e. open it in a web browser.
We’re still not educated enough (yet) to make it accessible a proper way, but we can access it by running some port forwarding magic:
kubectl port-forward workshop-frontend-868bbdb7f7-7fltf 8080:8080
Now you should be able to go to http://localhost:8080/ in your web browser and see some results. Don’t expect it to be fully functional, as we’re missing a pod for our backend, which is not the scope of this task.
Task: Check the logs
If something fails or whatever other reason, you can check your app’s logs by doing:
kubectl logs -f workshop-frontend-868bbdb7f7-7fltf
Task: Delete the pod
When creating a pod, a deployment is also created automatically (more under Deployment in this guide).
To delete the pod, we actually need to delete its deployment:
kubectl delete deploy workshop-frontend